When discussing the Cosmos, there is an important distinction between the “Cosmos Ecosystem” and the “Cosmos Hub.”
The Cosmos Ecosystem refers to the group of interconnected sovereign “hubs,” which are unique blockchain networks built using the same development toolkit as the original Cosmos Hub blockchain. These chains are usually connected through the Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol (IBC), which has allowed these chains to interact with each other natively to minimize use of bridges.
The Cosmos Hub (or Cosmos chain) is the central hub of the Cosmos ecosystem. It allows different blockchains to exchange data and assets with each other, enabling interoperability between them. ATOM is the native token of the Cosmos Hub and is used to secure the network and facilitate transactions on the hub.
Staking on The Cosmos Hub
The Tendermint consensus framework is a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm that allows the Cosmos Hub and its underlying blockchain “network of networks” to function. The Tendermint consensus gives users the ability to stake ATOM tokens, providing a steady stream of rewards independent of underlying token prices. Staking tokens helps decentralize, secure, and maintain the health of the network. Staking ATOM on the Cosmos Hub also gives users the opportunity to participate in network governance votes.
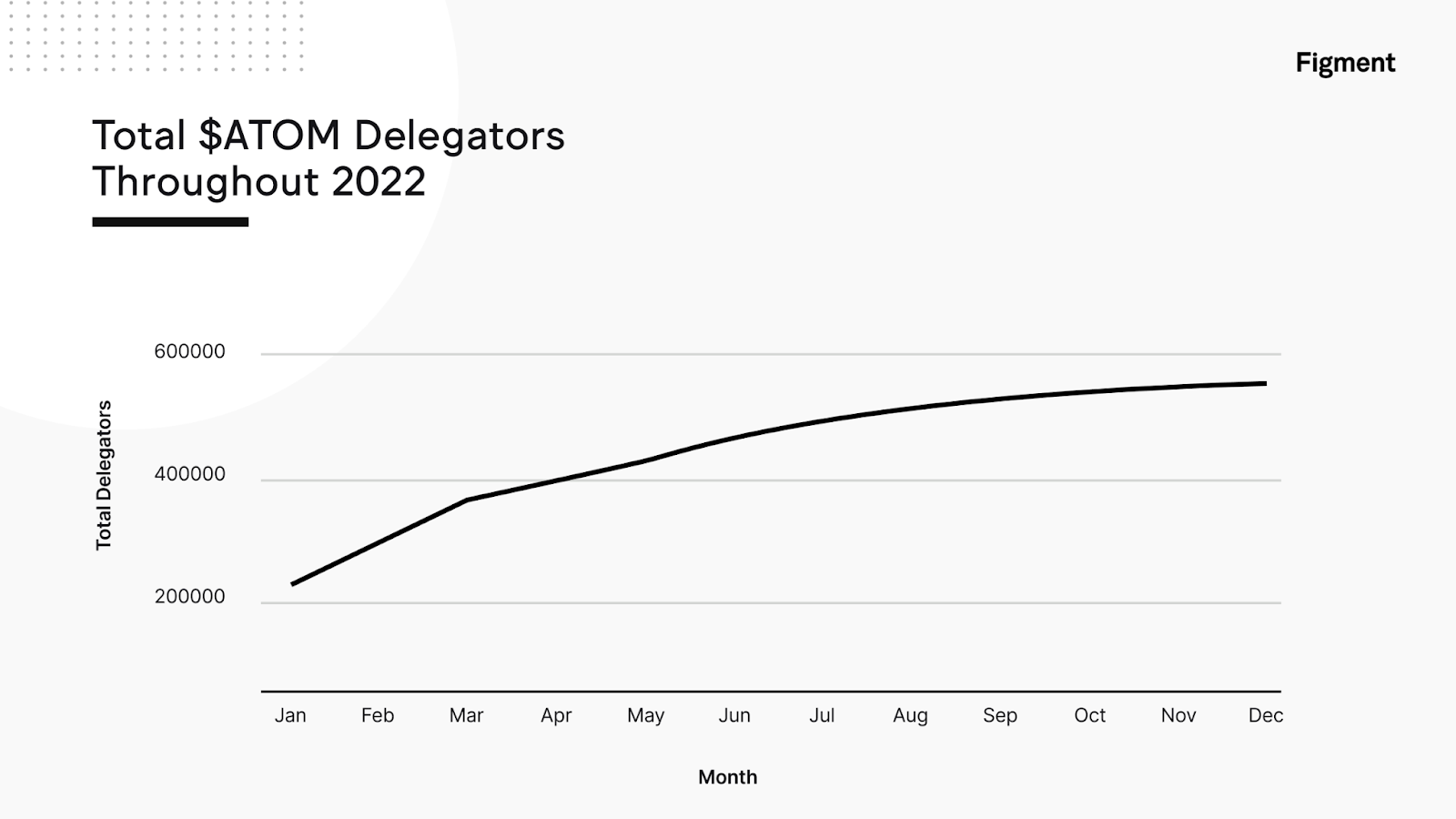
Throughout 2022, ATOM token delegations to Cosmos Hub validators have steadily increased. The increase in delegations over time is a positive indication of participation, decentralization, and overall network security for the Cosmos Hub. By locking tokens in the Cosmos Hub’s staking contract, delegators are placing faith in the long-term viability of the network.
Beyond the Hub: Core Areas of Development in the Ecosystem
Generally, development efforts in the Cosmos ecosystem can be categorized into four main areas: Interoperability, Scalability, Security, and Governance.
Interoperability
One of the biggest innovations of the Cosmos Ecosystem was IBC, which allowed chains in the ecosystem to communicate with each other natively. This ability to share data packets between chains in a permissionless way is more secure than traditional bridging models, and has the potential to connect non-Cosmos SDK chains as well.
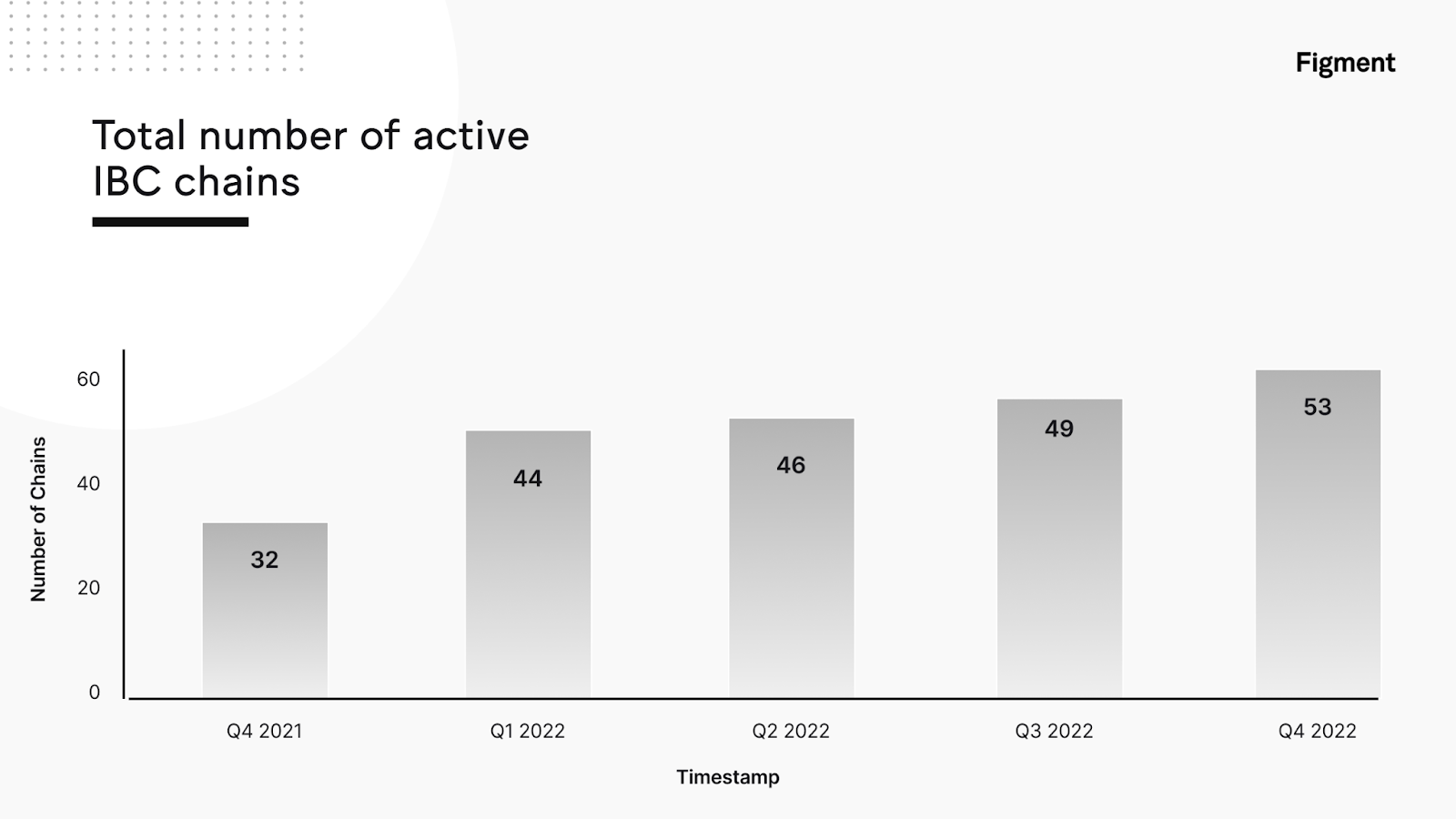
Despite the market movements throughout 2022, the total number of active IBC chains continued to rise:
A highly-anticipated new feature of the IBC framework is Interchain Accounts (ICA), which allows increased native functionality for account holders across IBC-connected networks. ICA represents a departure from commonly used bridging solutions.
ICA also enables cross-chain communication and chain-to-chain interactions, which function in the background similar to an “API” endpoint which can be called by another chain, executing the calls to these endpoints over the Interchain Account channel. This creates huge potential for interoperability, including Interchain NFTs. Most bridges, on the other hand, simply enable the passing of assets back and forth.
Scalability
The Cosmos SDK allows developers to build blockchains that can process transactions quickly and efficiently. This scalability can also enable a wider range of applications to be built on top of the Cosmos ecosystem. The new ICA feature also supports scalability and will allow blockchains to go from simply being able to transact with one another, to being able to execute transactions from one zone as local transactions on another. Additionally, the concept of a “data availability layer” is being championed by Celestia as a means of offloading more intensive actions away from base-layer chains. This will allow for more block availability and cheaper transactions as the ecosystem and IBC grow.
Security
As an ecosystem of application specific blockchains, Cosmos offers increased performance, security, and sovereignty. The Cosmos ecosystem is built on top of the Tendermint consensus algorithm, which is designed to provide strong security. The ecosystem faces a major upgrade to its security model through Interchain Security (ICS).
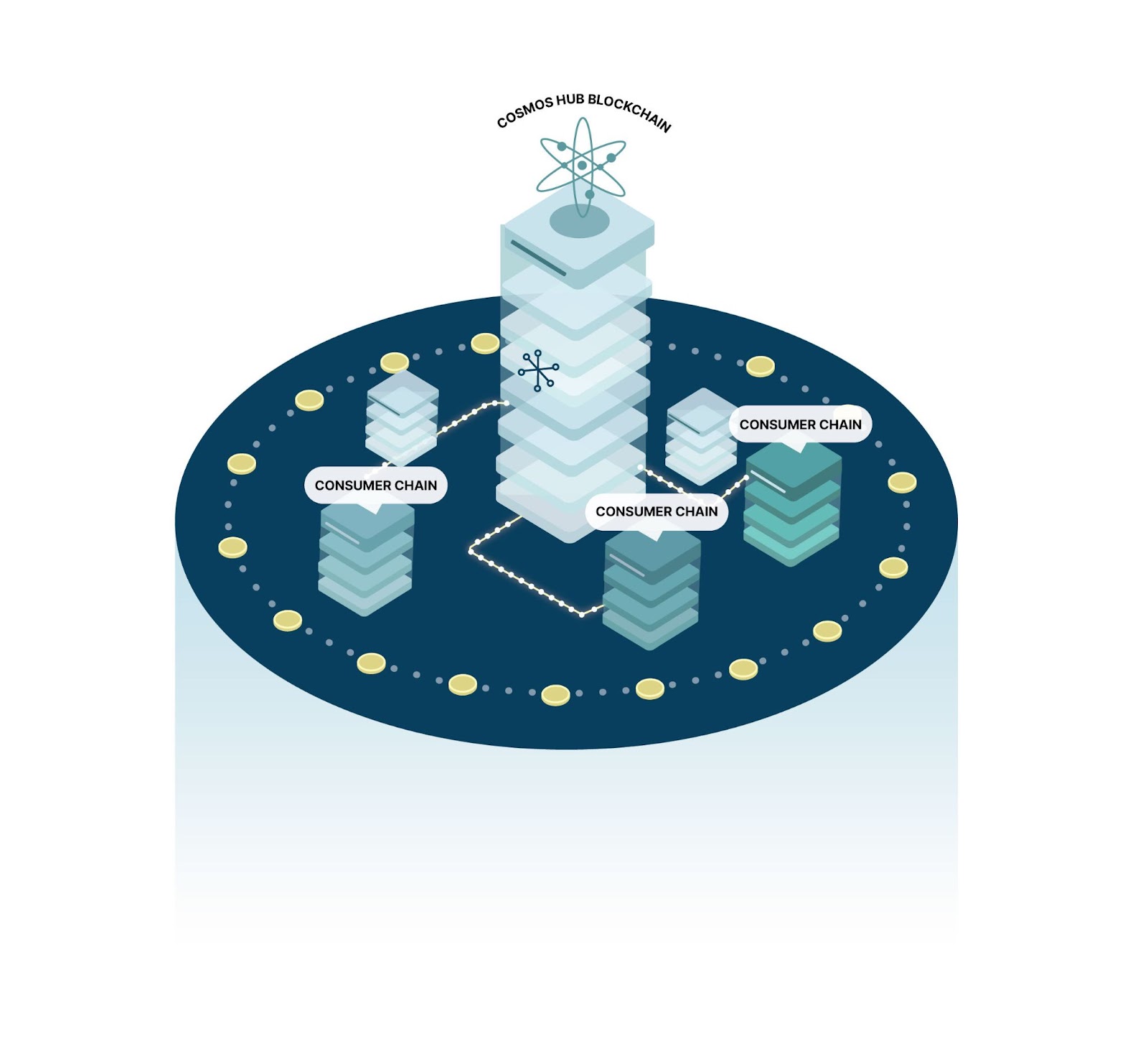
Interchain Security is set up so that a single network participant can support multiple channels of computation. The validators of an Interchain-secured zone operate validator nodes for both provider and consumer chains. Trust in Interchain Security comes from the fact that it is the same exact validator set that builds blocks on both chains, so validation and performance incentives remain consistent across all chains secured within the zone.
Governance
The Cosmos ecosystem has a decentralized governance model, which means that stakeholders in the network can vote on decisions related to the network’s development and direction. Cosmos chains currently use a pure-democratic “one-token-one-vote” system.
Osmosis: A Cosmonaut-approved DEX
Osmosis is one of the most popular decentralized exchanges (DEX) in the cosmos ecosystem. OSMO is the native token of the Osmosis DEX and is used for transaction fees, staking, liquidity, and more. With an average of over $250 million USD in IBC transfers each month and over 7.4 million OSMO traded on the DEX as recently as January 23.
Osmosis is the largest chain in the Cosmos ecosystem by Total Value Locked (TVL). Osmosis features “superfluid staking,” a reward-generation method that enables liquidity providers to receive additional rewards by staking pooled assets.
The most recent Osmosis upgrade was V14 (Neon) which went live January 23, 2022.
Key Components:
- “Geometric TWAP” (which stands for “Time Weighted Average Pricing”), will result in asset pricing that is less sensitive to price manipulation relative to other methods of averaging asset prices, and increases the cost to manipulate asset prices by attackers.
- “Downtime Detection Module” will enable connected smart contracts to query data related to downtime on Osmosis, which will help prevent exploits or improper liquidations if data received from Osmosis is incorrect as a result of downtime.
- “IBC v4.2.0 and Wasm Hooks” is an upgrade that allows, among other things, reusable cross-chain wasm hooks. These allow Osmosis to establish “outpost dexes” to allow other protocols to process swaps within their own interface while using Osmosis liquidity.
Future Features/Upgrades:
- “Concentrated Liquidity” – A feature pioneered by Uniswap that allows liquidity providers to concentrate their capital only at certain limited asset price ranges (i.e. providing USDC liquidity only between $0.99 – $1.01 USD).
- “Mars Protocol” – A smart-contract lending protocol that will be integrated with Osmosis at launch to enable “outpost dexes” throughout the Cosmos ecosystem.
- “protoRev module” – A MEV (Maximum Extractable Value) solution approved through Proposal #341 pioneered by Skip protocol to capture arbitrage revenue on Osmosis.
Despite the rich amount of features related to trading and providing liquidity, the staking ratio of OSMO is strong at ~41% of total assets, making this chain highly secure. The dynamic Osmosis has between maintaining this strong level of security and interoperability makes it a great case study of what is possible in the Cosmos ecosystem.
Other Notable Ecosystem Projects
The following recent projects in the ecosystem demonstrate this increased focus on base principles and interchain functionality:
- Celestia: An IBC-native, data availability protocol that boasts compatibility with other chains.
- Composable Finance: Composable Finance is building the infrastructure to interconnect the Cosmos and Polkadot ecosystems through the BEEFY light client and a novel cross-chain smart contracting platform called XCVM.
- Penumbra: Penumbra is the first non-Cosmos SDK chain to connect to the IBC testnet.
- Polymer: Using zero-knowledge proofs, Polymer aims to connect IBC-enabled chains with non-IBC chains.
- Quicksilver: One of the earliest adopters of Interchain Accounts, Quicksilver is the ecosystem’s foremost liquid staking solution. This protocol allows stakers to continue earning rewards while maintaining the liquidity aspects of their tokens.
- Stargaze: This protocol is secured by proof-of-stake and is the main NFT marketplace in the Cosmos ecosystem. Quicksilver has been integrated as a means of earning staking rewards on the native token, STARS, while maintaining token liquidity in order to purchase NFTs if desired.
Staking with Figment
As the Cosmos ecosystem continues to grow and evolve with new projects, the underlying Cosmos Hub protocol remains strong with a steady growth in staking delegations.
Staking in the Cosmos ecosystem is a powerful way for users to earn rewards while contributing to the security and stability of the networks found there. By staking ATOM, OSMO, or other tokens within the Cosmos ecosystem, users can participate in governance and earn a share of the network’s inflationary rewards.
If you are interested in staking ATOM, OSMO, or other Cosmos ecosystem assets like EVMOS, SCRT or STARS – Figment offers a host of services aimed at delivering safe and reliable staking rewards. Figment is the world’s leading provider of blockchain infrastructure. Our 200+ institutional clients rely on us to provide best-in-class staking services including seamless and easy integrations, complete staking coverage, detailed rewards reporting, insights, enterprise-grade liquid staking, and more.
Figment’s Protocol team has extensive knowledge on the Cosmos ecosystem intended to help dive into the specifics such as governance and staking information. Contact us to learn more about staking in the Cosmos ecosystem.



